√ダウンロード T11-t12 Nerve Distribution 172562-T11-t12 Nerve Distribution
#2 Currently, T12L1 is considered a thoracic level for both transforaminal and facet injections For transforaminal approach at T12L1, this is considered thru the T12 foramen where the T12 spinal nerve exits For facet joint blocks, the T12L1 facet joint receives innervation from the T11 and T12 medial branchesSegmental branches of T11, T12, T13, L1, L2, and L3 were adequately stained in %, 60%, 100%, 100%, 90%, and 30% of injections, respectively Conclusions and clinical relevance This anatomical study suggests that the transversus abdominis plane (TAP) block would provide adequate regional anesthesia of the abdomen, potentially extending to the We sent the patient for electromyography that showed acute denervation changes in the T11–T12 distribution Nerve conduction was normal in the dermatomes above and below the affected areas We diagnosed a postherpetic pseudohernia After three months, the bulge had improved but not resolved completely
1
T11-t12 nerve distribution
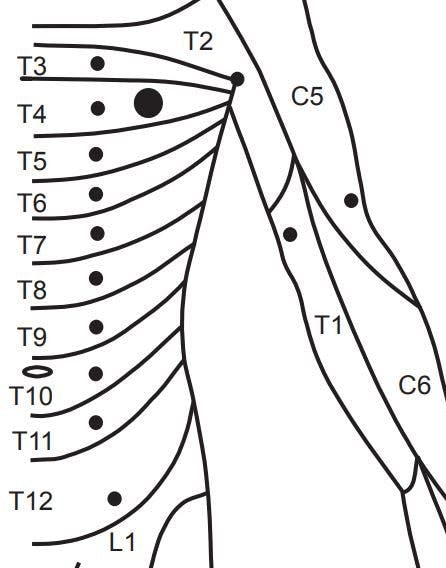
T11-t12 nerve distribution-T12 anteriorly just superior to the pelvic girdle; The next area to cover is the chest and back (torso) The dermatomes of this area are innervated by T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12 The apex of the axilla is innervated by the T2 nerve root The T3 nerve root will supply the area where the midclavicular line and third intercostal space intersect



What Happens When The Dorsal Root Is Damaged Quora
The Celiac Plexus is made up of 15 ganglia carrying afferent fibers from the upper abdominal organs (stomach to mid transverse colon, including pancrease and gallbladder) as well as sympathetic preganglionic fibers from greater (T5T10), lesser (T10T11), and least (T12) splanchnic nerves The plexus is located in the upper abdomen typically at the level of the L1 Subcostal Nerve (T12), Iliohypogastric (T12L1), Ilioinguinal (L1), and Genitofemoral (L1L2) (Table 351) The cutaneous sensory innervation of the abdomen/flank and motor innervation to the rectus abdominis/external oblique are by the subcostal nerve Beside above, what does t11 nerve control? Lumbar spine imaging failed to reveal compressive nerve root pathology Electromyography, nerve conduction studies, and muscle and nerve biopsy suggested a preganglionic lesion and ruled out a peripheral cause Upper spine magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) revealed significant spinal stenosis at C4C7 and T11T12
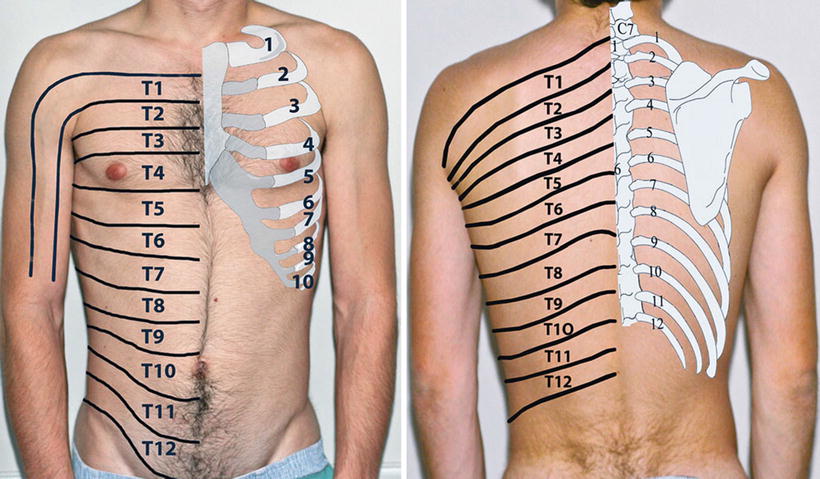
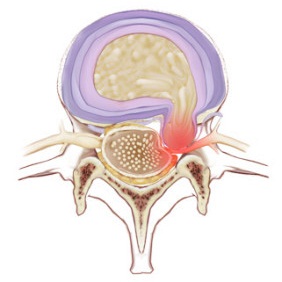
The intercostal nerves originate segmentally from the anterior/ventral rami of thoracic spinal nerves T1 to T11 The term ’intercostal’ refers to their course in the intercostal space, in which they run alongside intercostal vesselsThe anterior rami of the most inferior thoracic spinal nerve (T12) gives rise to the subcostal nerve which runs inferior to the twelfth rib, theFigure 8A (Left) Noncontrast MRI Scan demonstrating a large Far Left Lateral Herniated Thoracic Disc (Wide Oblique Arrow) at the T11T12 level The Nerve Root is compressed and the Spinal Cord (Curved Arrow) is displaced to the opposite (Patient's RIGHT) side of the Spinal CanalCompression fractures of the spine usually occur at the bottom part of the thoracic spine (T11 and T12) and the first vertebra of the lumbar spine (L1) Compression fractures of the spine generally occur from too much pressure on the vertebral body This usually results from a combination of bending forward and downward pressure on the spine
Approach SL stained T11, L1 and L2 in 100% of injections and T9, T10, T12 and T13 were stained in 375%, 875%, 75% and 625% of injections, respectively Approach SL resulted in greater staining of nerves cranial to T12 compared with approach LL The two approaches were equivalent in staining nerves caudal to T12P < 005, vs T12) In the ChG T12, the percentages of labeled cells were 1686% ± 263% and 2351% ± 713% for RPI and CPI sections, respectively We counted few FGlabeled cells in these ganglia in the control 0 #2 T9, T10 medial branches innervate T1011 T10, T11 medial branches innervate T11T12 So this would represent 2 facet levels treated with modifier RT Destruction by neurolytic agent, paravertebral facet joint nerve (s), with imaging guidance (fluoroscopy or CT);




Abdominal Wall Pain Clinical Evaluation Differential Diagnosis And Treatment American Family Physician
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/overview_image/1041/2WGMH7h85ERXSSS2nsroA_anatomy-pns-dermatomes.jpg)



Intercostal Nerves Origin Course And Function Kenhub
The thoracic spinal nerve 12 (T12) is a spinal nerve of the thoracic segment It originates from the spinal column from below the thoracic vertebra 12 (T12) It may also be known as the subcostal nerve References This page was last edited on 12 February 18, at 0046 (UTC)Methods The 71yearold female patient clinically presented with radicular pain of beltlike distribution in the T8 dermatome on both sides, rachialgia, kyphoscoliosis and T12 (12th Thoracic Vertebra) The twelfth thoracic vertebra (or the T12 vertebra) is the largest and most inferior of the thoracic vertebrae T12 bears the most weight of any thoracic vertebra, making it the strongest thoracic vertebra, but also the most susceptible to stressrelated injuries In many ways, the T12 is a hybrid vertebra with the




Thoracic Spinal Nerve 11 Wikipedia
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/l1-dermatome-1/iNOHSCWu3z1VMhb4v4RRA_L1.png)



Dermatomes Anatomy And Dermatome Map Kenhub
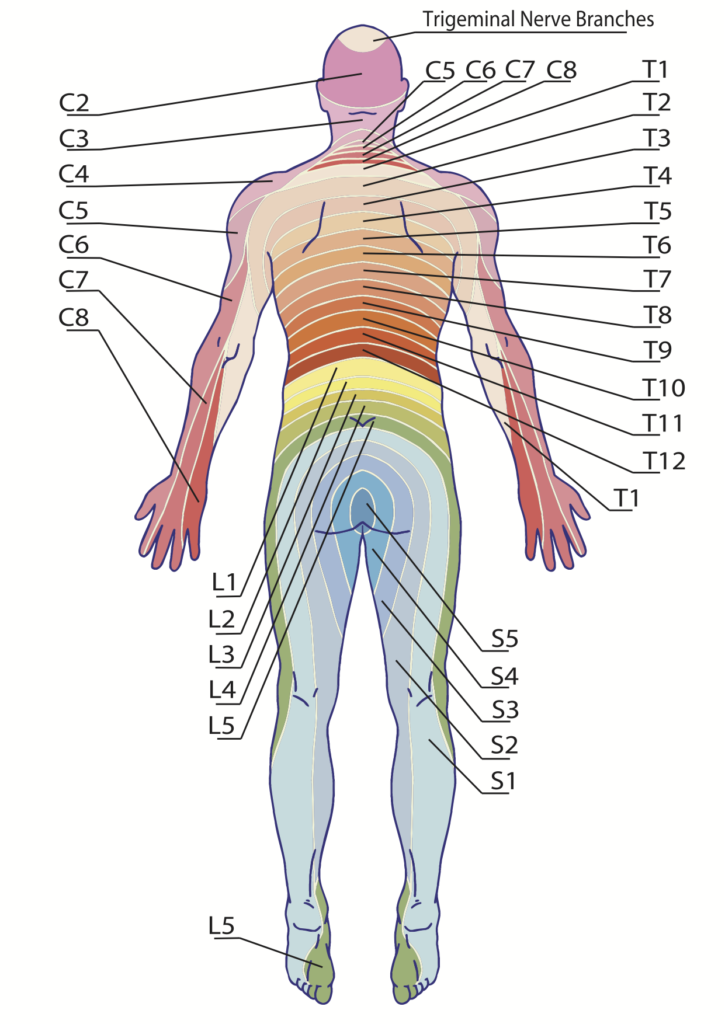
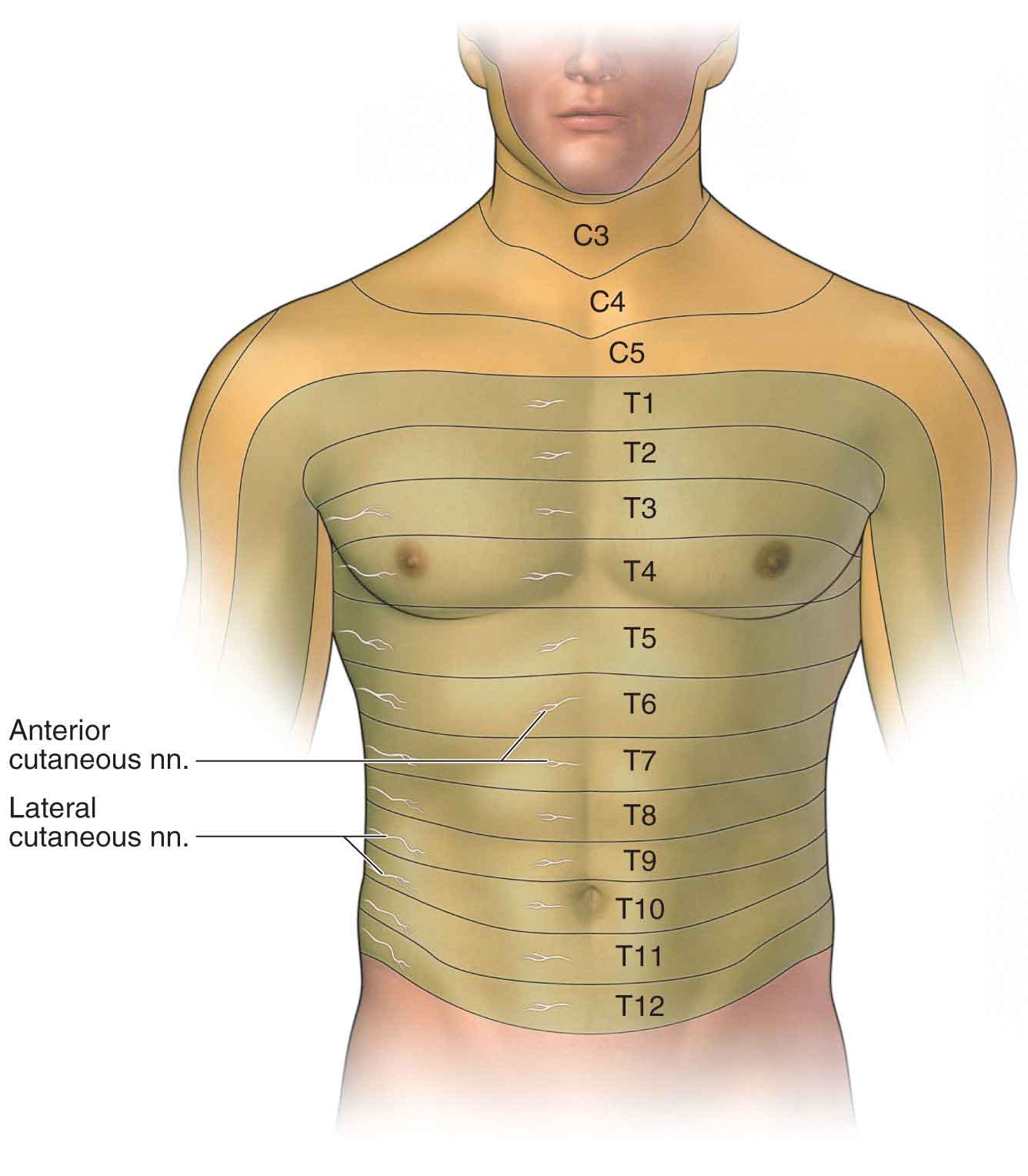
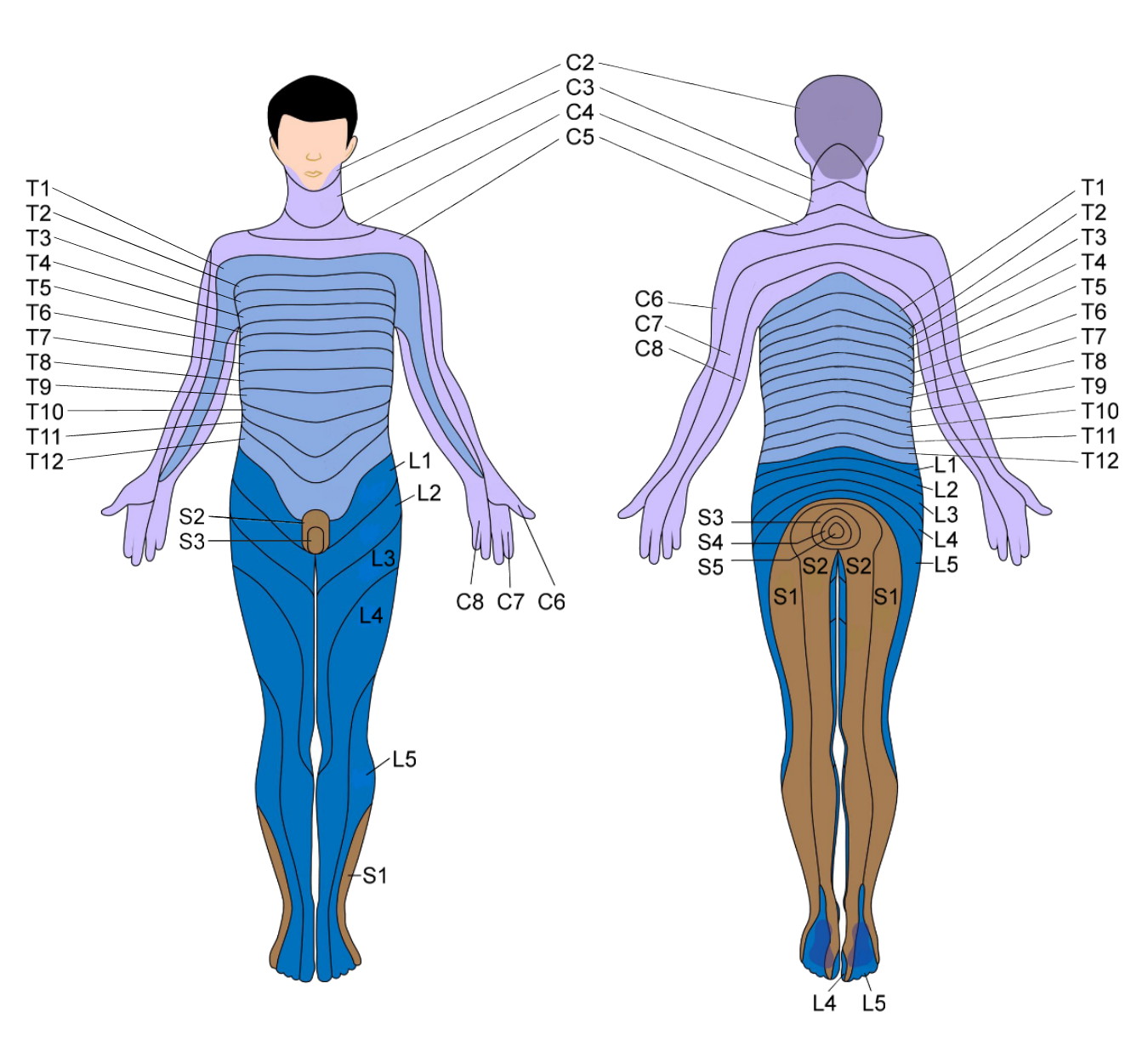
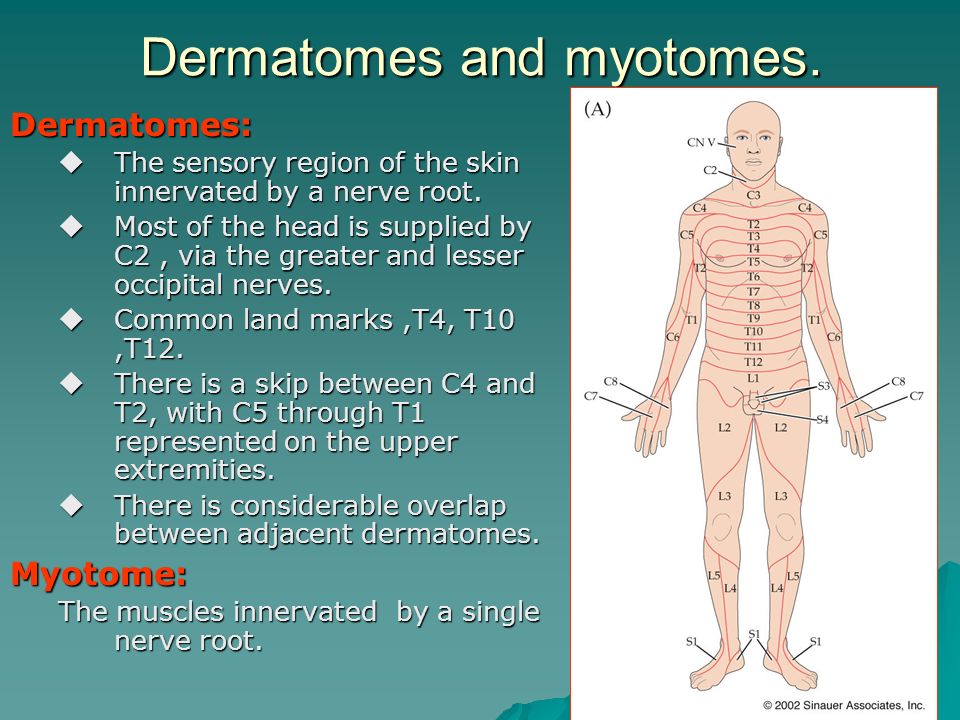
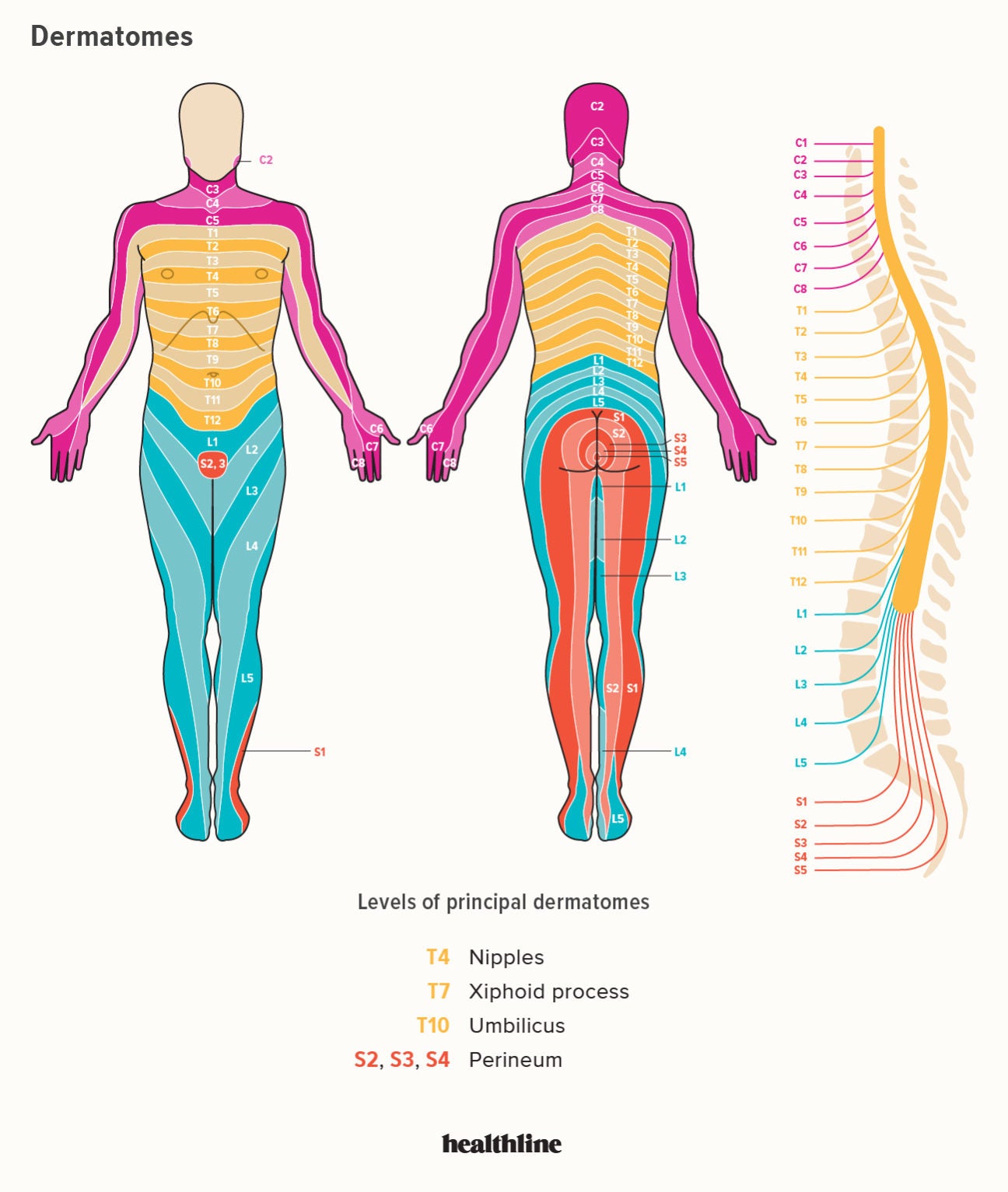
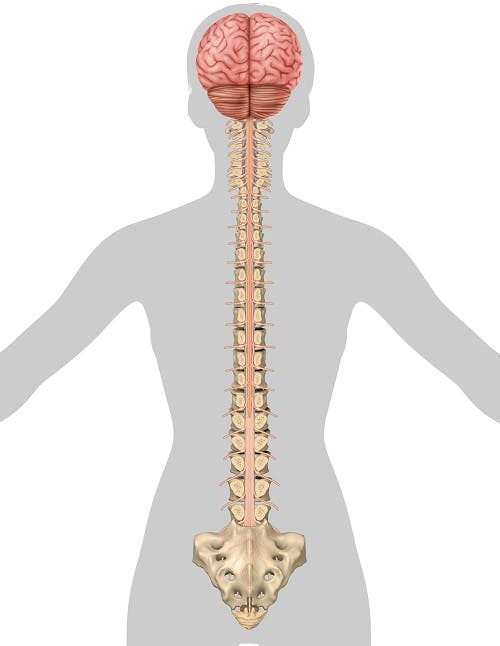
Duodenum The dermatome pain referral for the T7 spinal nerve traverses from the 7th segment, anteriorly along the 7th & 8th rib and terminates slightly inferior of the xiphoid process T8 The origin of the syndrome is a segmental dysfunction of T12 –;A dermatome is an area of skin that is mainly supplied by afferent nerve fibres from the dorsal root of any given spinal nerve There are 8 cervical nerves (C1 being an exception with no dermatome), 12 thoracic nerves, 5 lumbar nerves and 5 sacral nervesEach of these nerves relays sensation (including pain) from a particular region of skin to the brain



3



Cervical Disc Herniation Contact Us On 61 2 6724 To Book In A Consultation
T11 Between the level of the belly button and the groin (inguinal ligament) T12 The midpoint of the groin 5 lumbar dermatomes (L1L5) that supply sensation from these spinal nerves in the lower limb (C6C8) or anywhere along the distribution of the nerve through the right upper limb (arm or hand)A T11 injury will demonstrate itself by severe back and leg pain If the nerves in the T11 vertebrae are damaged, common symptoms include weakness and numbness in these areas T12 Vertebrae Pain Symptoms Like the other transition vertebrae, T12 vertebra pain symptoms involve severe to moderate back pain depending on the seriousness of the injury T12 The T12 vertebra is the twelfth thoracic vertebra in the spine of the human body It is part of the spinal column, which supports the top of the human body The spinal column extends from the



Intercostal Nerve Blocks Radiology Key



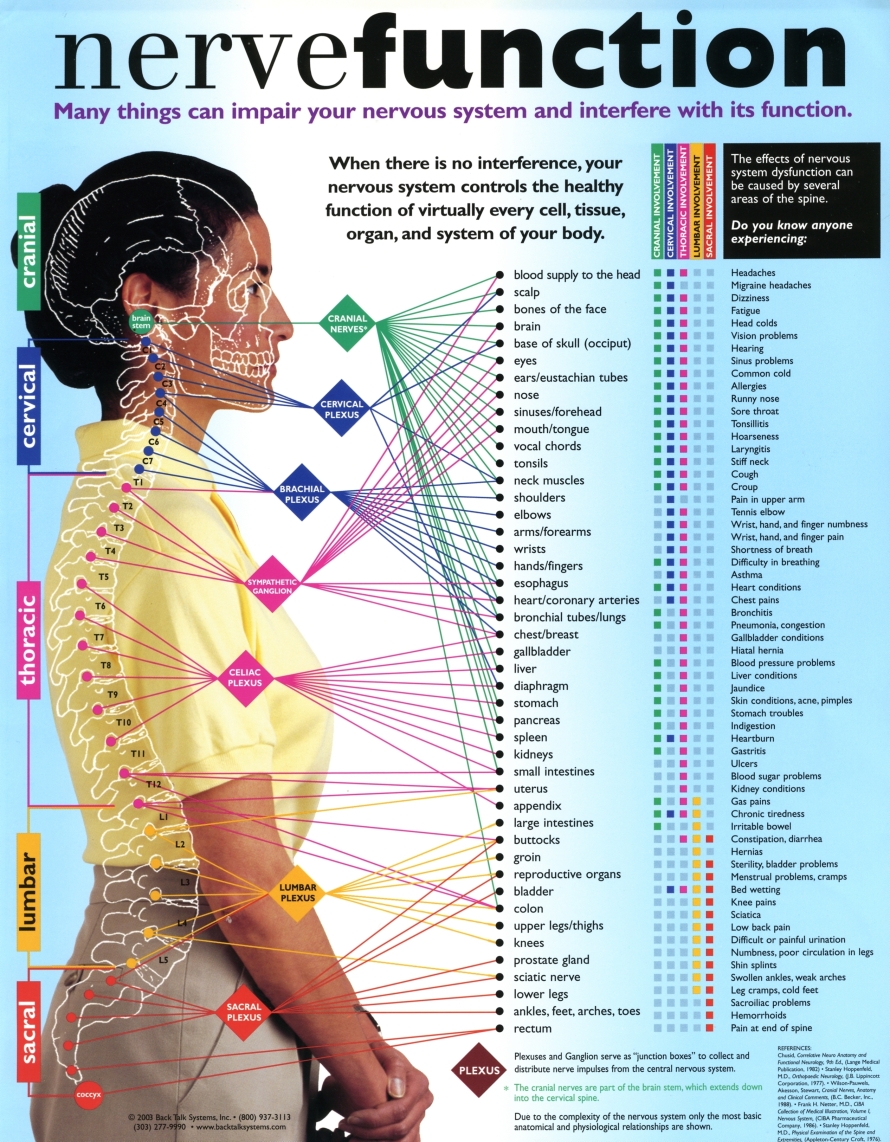
The Nervous System Musculoskeletal Key
Like all of its spinal counterparts, T11 protectsThe thoracic spine is made up of twelve vertebrae, known as T1 through T12 It is located between the cervical and lumbar levels, right in the middle of the spine at your midback These twelve vertebrae and nerves connect directly to the rib cage, thus allowing easy communication with the central parts of the bodyMethods The clinical features of 26 patients who had undergone operations for single disc herniations at T10T11 through L2L3 were investigated Affected levels were as follows 2 patients with disc herniation at T10T11 disc, 4 patients at T11T12, 3 patients at T12L1, 6 patients at L1L2, and 11 patients at L2L3




Life Science Bio Classes Chapra Bihar Spinal Nerve Distribution Facebook



Thoracic Spinal Nerves Physiopedia
T10 T12 Nerves Neuritis Neuritis of the spinal accessory nerve, the long thoracic nerve and the suprascapular nerve can provoke unilateral pain at the base of the neck and over the scapula Herpes zoster In that the thorax is often the seat of a herpes zoster infection, unilateral spontaneous pain of recent onset always calls for aCervical or thoracic, single facet joint Maigne syndrome is defined as dysfunction of the thoracolumbar junction marked by pain in the territory of the associated dermatomes of T11L1 or 2 Background Anatomy The T12 and L1 ventral rami (subcostal & illiohypogastric nerves respectively) give rise to the lateral cutaneous branch over the lateral aspect of the hip, which terminates at




Anatomy Of Splanchnic Nerves And Celiac Plexus Figure Adapted From Download Scientific Diagram



Radicular Syndrome Darwin Amir Bgn Ilmu Penyakit Saraf Ppt Video Online Download
The Celiac Plexus is made up of 15 ganglia carrying afferent fibers from the upper abdominal organs (stomach to mid transverse colon, including pancrease and gallbladder) as well as sympathetic preganglionic fibers from greater (T5T10), lesser (T10T11), and least (T12) splanchnic nerves The plexus is located in the upper abdomen typically at the level of the L1 I also had herniation at t11 and t12 a 5mm hernation to the left, my back never hurt my left side hurt me so bad I thought I was having a kidney stone, my dr Sent me for a mri immediately as I was an xray tech,the pain management dr did 3 injections 2 weeks apart and used the carm to see exactly where he was injecting I went 10yrs pain free and a week ago I fell and Problems caused by a T12 Subluxation A subluxation is a minor misalignment of the spine causing nerve interference Your body communicates from the brain through the spinal cord, spinal nerves and peripheral nervous system Your body communicates back to the brain through your nervous system Your nerves are like wires but much more delicate



Section 2 Chapter 4 Pain Generators And Pathways Of Degenerative Disc Disease Wheeless Textbook Of Orthopaedics



Thoracic Spinal Nerves Physiopedia
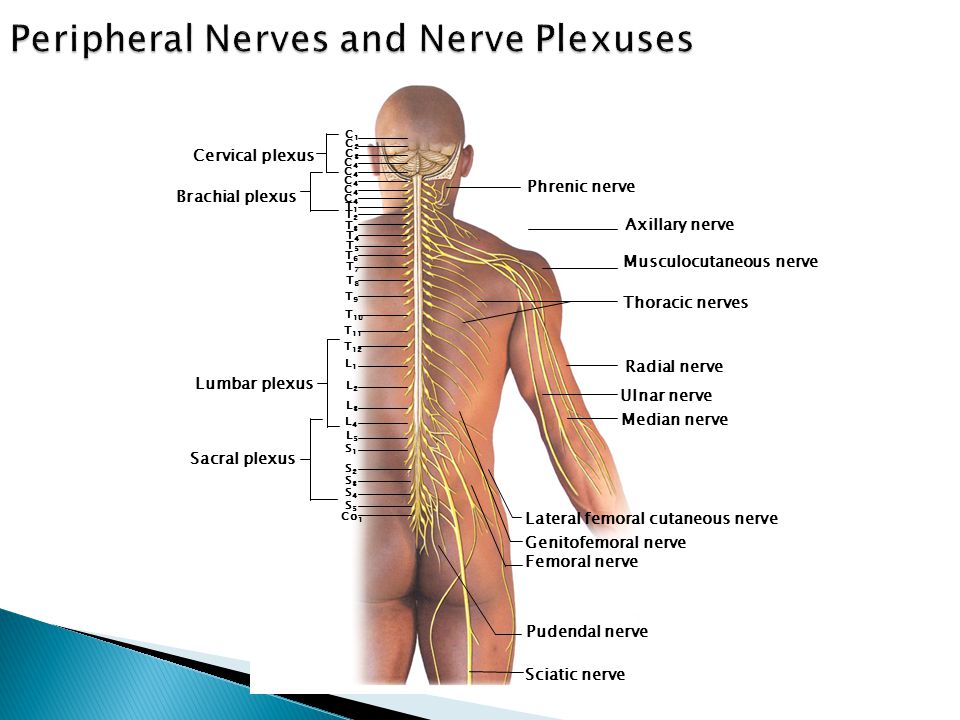
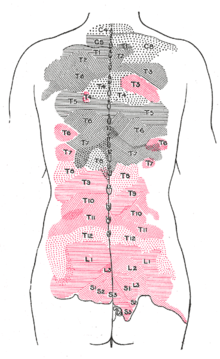
Conclusions and clinical relevance Staining of T11–T14 nerves was the same in both treatments but the higher volume stained more T9–T10 nerves Based on dye distribution, a rectus sheath block may only provide ventral abdominal analgesia cranial to the umbilicus in pigs",Description The twelve thoracic nerves T1T12 emerge below T1 and T12, respectively The roots of the thoracic nerves, with the exception of the first, are of small size, and the posterior only slightly exceed the anterior in thicknessThey increase successively in length, from above downward, and in the lower part of the thoracic region descend in contact with the medullaT11 dermatome 11th intercostal space T12 dermatome Inguinal ligament L1 dermatome 1/2 distance between T11&T12 L2 dermatome Mid anterior thigh L3 dermatome Medial femoral condyle L4 dermatome Medial malleolus L5 dermatome Dorsum of foot at 3rd MP joint S1 dermatome Lateral border of foot



Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury Nature Reviews Disease Primers




Human Dermatomes Sciencedirect
The distance between the longitudinal references for normalization (the T11T12 disk and the L5S1 disk) ranged from 1 to 224 cm Longitudinal distribution of average axial section area at sites along the length of the dural sac are shown in Figure 4, comparing all (Figure 4(A)), and slim and obese subjects (Figure 4(B)) The section areaLower limbs and genitalia The dermatomes of the lower limbs are distributed in spiral arrangements with segments L1S5 This is because of how the limbs rotate to adapt an erect position during development Also, unlike other thoracic vertebrae, T11 features a spinous process that is relatively short, and it tends to be horizontal, featuring only a slight




1 Establishment Of Microsurgical Anastomoses Between T11 T12 And Download Scientific Diagram




Dermatomes Vector Illustration Labeled Educational Anatomical Skin Parts Stock Vector Image By C Vectormine
Radiculopathy is produced by compression or irritation of a nerve root within the spinal column less than 5% of disc herniations The most common location for disc herniation in the thoracic spine is at T11T12 12 present in 67% of patients 29 The pain of radiculopathy tends to follow a dermatomal distribution and is worsened by Join Date Nov 10 Location USA Posts 9,238 Re T11 T12 Thecal Sac compression Welcome to the board Sorry you are having additional problems since your surgery The L5S1 disc bulge correlates to the symptoms you describe It is the likely source of pain in the lower back, buttock, leg, etc The L5 nerve innervates those three middle toes Differential Distribution of Renal Nerve Cells in SrG and ChG from the Rostral and Caudal Poles of the Kidney T10, T11, L1, L2;




Avoiding Abdominal Flank Bulge After Anterolateral Approaches To The Thoracolumbar Spine Cadaveric Study And Electrophysiological Investigation In Journal Of Neurosurgery Spine Volume 15 Issue 5 11 Journals



How To Prevent And Alleviate Spinal Degeneration Clinical Somatics
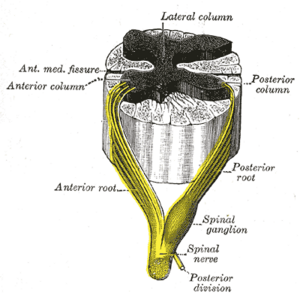
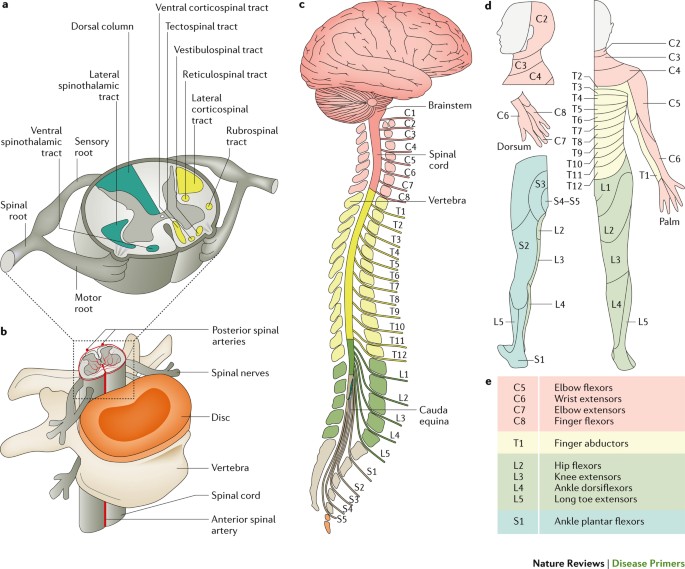
The most common symptom is pain referred to structures innervated by the dorsal rami of the T11, T12 and L1 spinal nerves 3, 10, 15, 32 Both the central and peripheral variants of Maigne Syndrome may produce pain referred to the lower back,L1, and sometimes T11 T12 or L1 L2 The segment is painful to specific pressures, and palpation reveals soft tissue changes in the territory of the innervation of the corresponding rachidian nerve (T12, L1)Respectively The anterior and posterior nerve roots combine on each side to form the spinal nerves as they exit the vertebral canal through the intervertebral foramina or neuroforamina The 31 spine segments on each side give rise to 31 spinal nerves, which are composed of 8 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral, and 1 coccygeal spinal nerve



1



T9 T12 Vertebrae Thoracic Spinal Cord Injury Spinalcord Com
Dermatomes A dermatome is an area of skin which is chiefly supplied by a single spinal nerve There are 8 cervical nerves (C1 denoting an anomaly with no dermatome), 12 thoracic nerves (T1T12), 5 lumbar nerves (L1L5) and 5 sacral nerves (S1S5) Each of these nerves relays sensation (including pain) from a particular region of skin to the brainT11–T12 distribution Nerve conduction was normal in the dermatomes above and below the affected areas We diagnosed a postherpetic pseudohernia After three months, the bulge had improved but not resolved completely Muscle weakness related to herpes zoster represents a protrusion of the abdominal wall without an actual defect in the muscleT7 NONE Intercostals of Respective Levels;



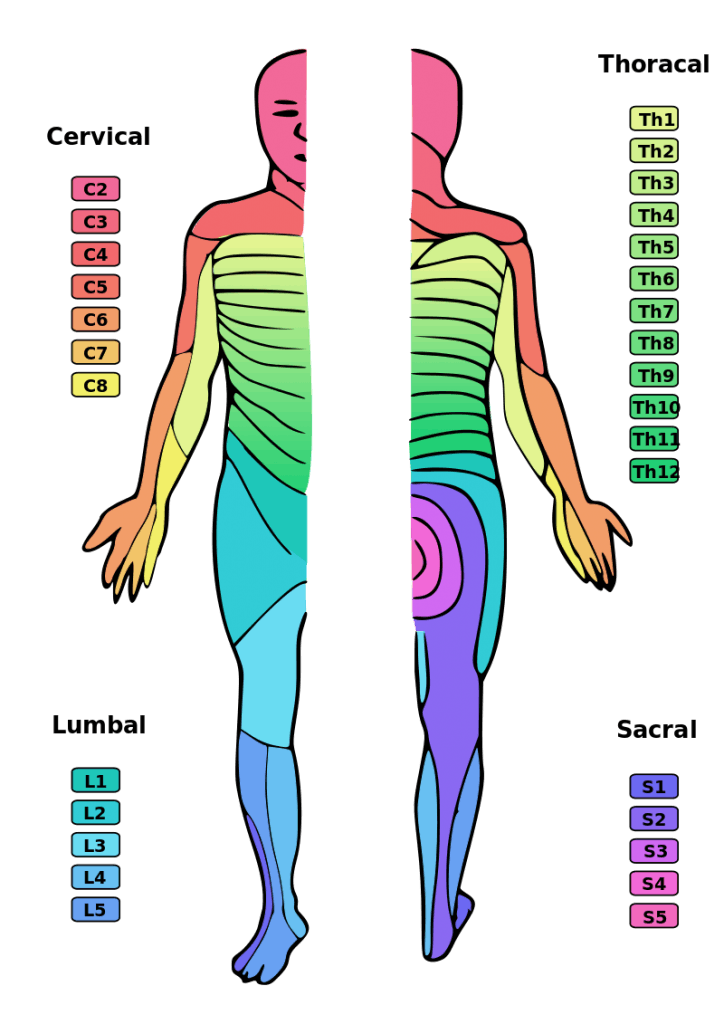
Dermatomes Definition Chart And Diagram
/spinalregions-2ab9b0b86f0f4705bdbdd63636f7ca84.jpg)



Dermatomes What They Are Where They Are What They Do
T11 evenly distributed anteriorly between T10 and T12 dermatomes; Surgery at the T12L1 level with burning pain into the sole of the foot would mean to me injury to the S1 nerve or possibly L5 since these nerves exit the cord at about T910 level A spinal cord stimulator (SCS) can be implanted above the level of the fusion and directed either up or down depending upon the coverage necessary T12 spinal cord injury patients generally have full function in their upper limbs and trunk The T12 nerve roots innervate the very lower abdominal muscles Therefore, individuals with T12 SCIs will focus on rehabilitation for the lower half of their body



Bats Better Anaesthesia Through Sonography




How Do Dermatomes Work Map Myotomes Vs Dermatomes
However, Alamán et al described the distribution of the dye along the sympathetic chain and the spinal nerves (T11–T13 and T12–T13, respectively), suggesting that the dye solution could travel through the paravertebral compartments The genitofemoral nerve was stained in
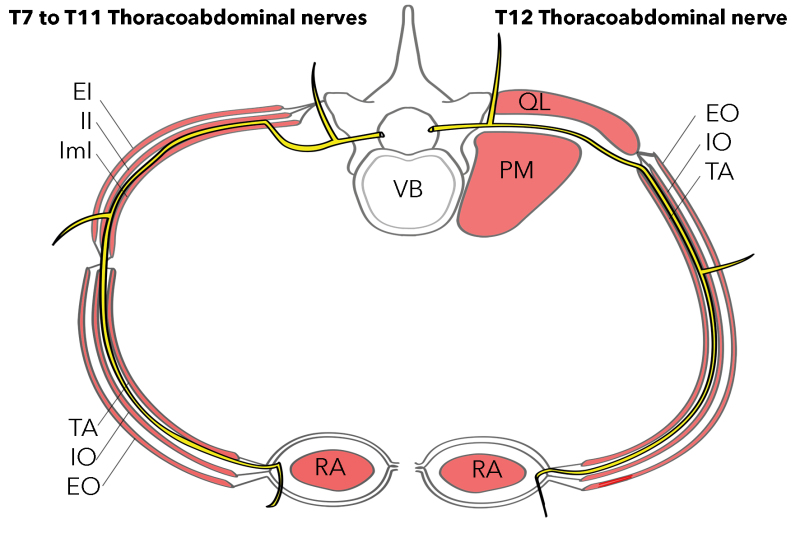



Figure T7 To T11 Thoracoabdominal Nerves Statpearls Ncbi Bookshelf




The Thoracic Level Chapter 3 Spine Disorders




Subcostal Nerve Wikipedia



Numbness And Tingling And Burning Oh My



T12 Spinal Cord Injury What Is The Recovery Outlook Flint Rehab



Chapter 8 Spinal Nerve Roots Ppt Video Online Download



Intercostal Nerve Entrapment Abdomen Springerlink



Spinal Nerve Wikipedia




Postureology The Science Of Looking And Feeling Your Best Spine Health Medical Massage Therapy




Low Back And Leg Pain Is Lumbar Radiculopathy




Anatomyof The Vertebral Column And Spinal Cord Chapter 56 Essential Clinical Anesthesia
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/intercostal-nerve/bCNBMEuoT4FxpsSP2BnmA_Intercostal_nerves.png)



Intercostal Nerves Origin Course And Function Kenhub
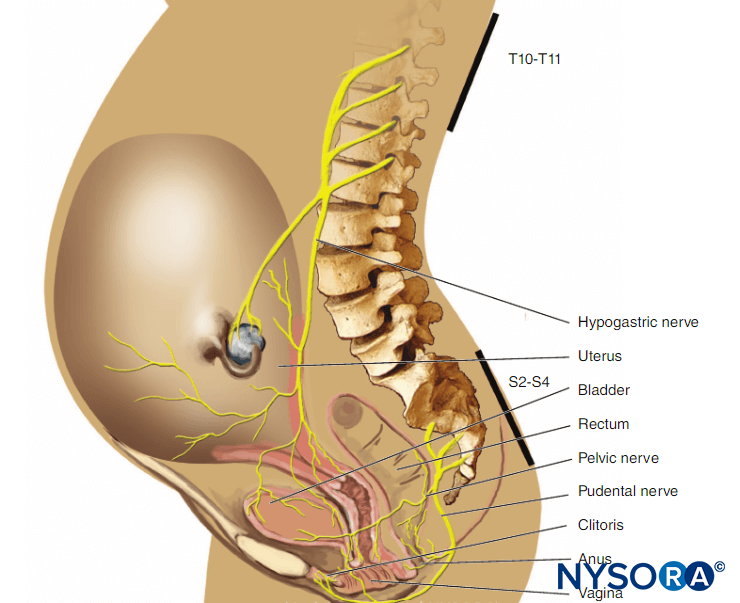



Obstetric Regional Anesthesia Nysora Nysora




Functional Regional Anesthesia Anatomy Nysora Nysora



1
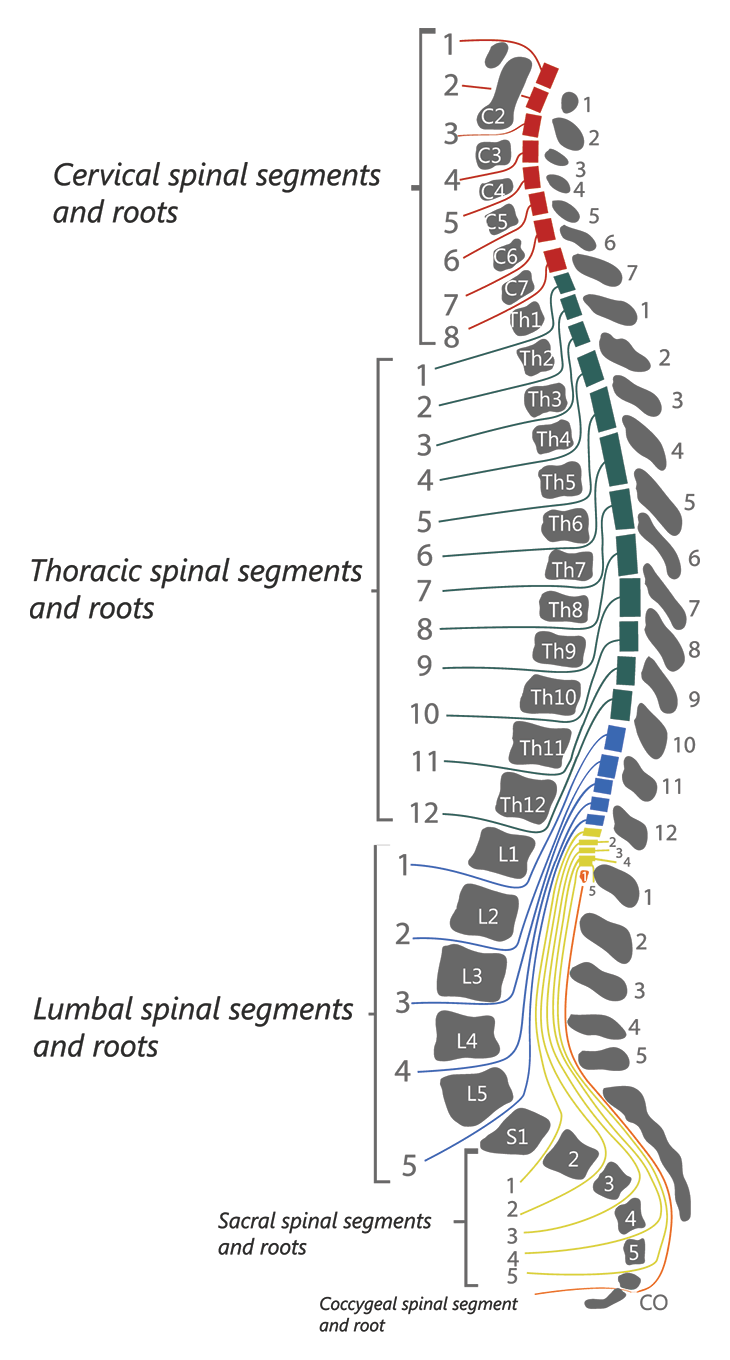



Spinal Cord Injury Levels Classification
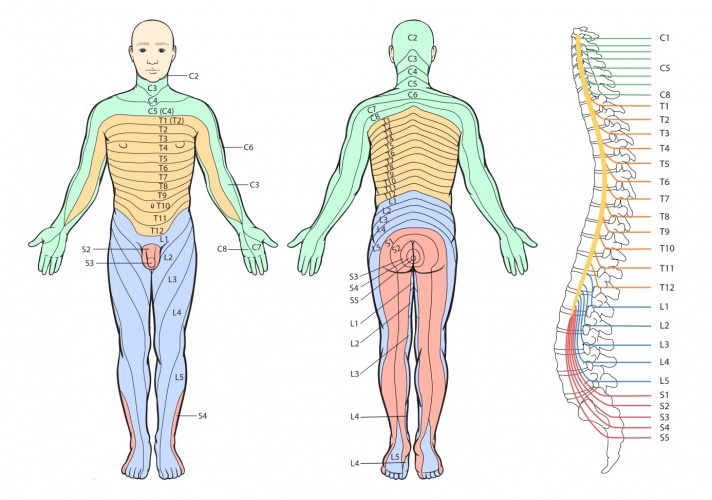



Thoracic Radiculopathy Physiopedia
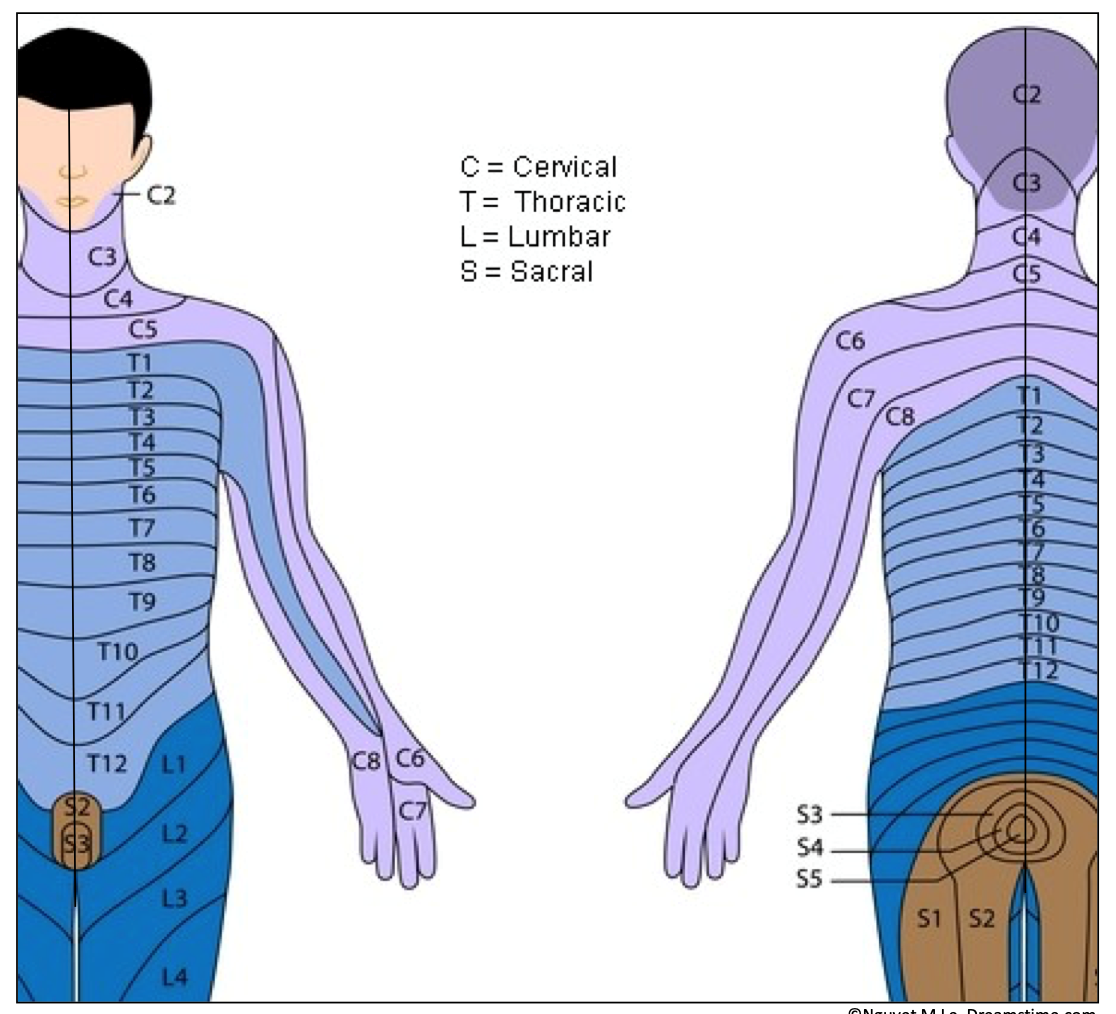



Dermatomes And Myotomes




Thoracic Spinal Nerves




Intercostal Nerve Block Landmarks And Nerve Stimulator Technique Nysora Nysora




Spinal Nerves Boundless Anatomy And Physiology




Intraoperative View A Of The Perineural Cyst At The Left T11 Nerve Download Scientific Diagram
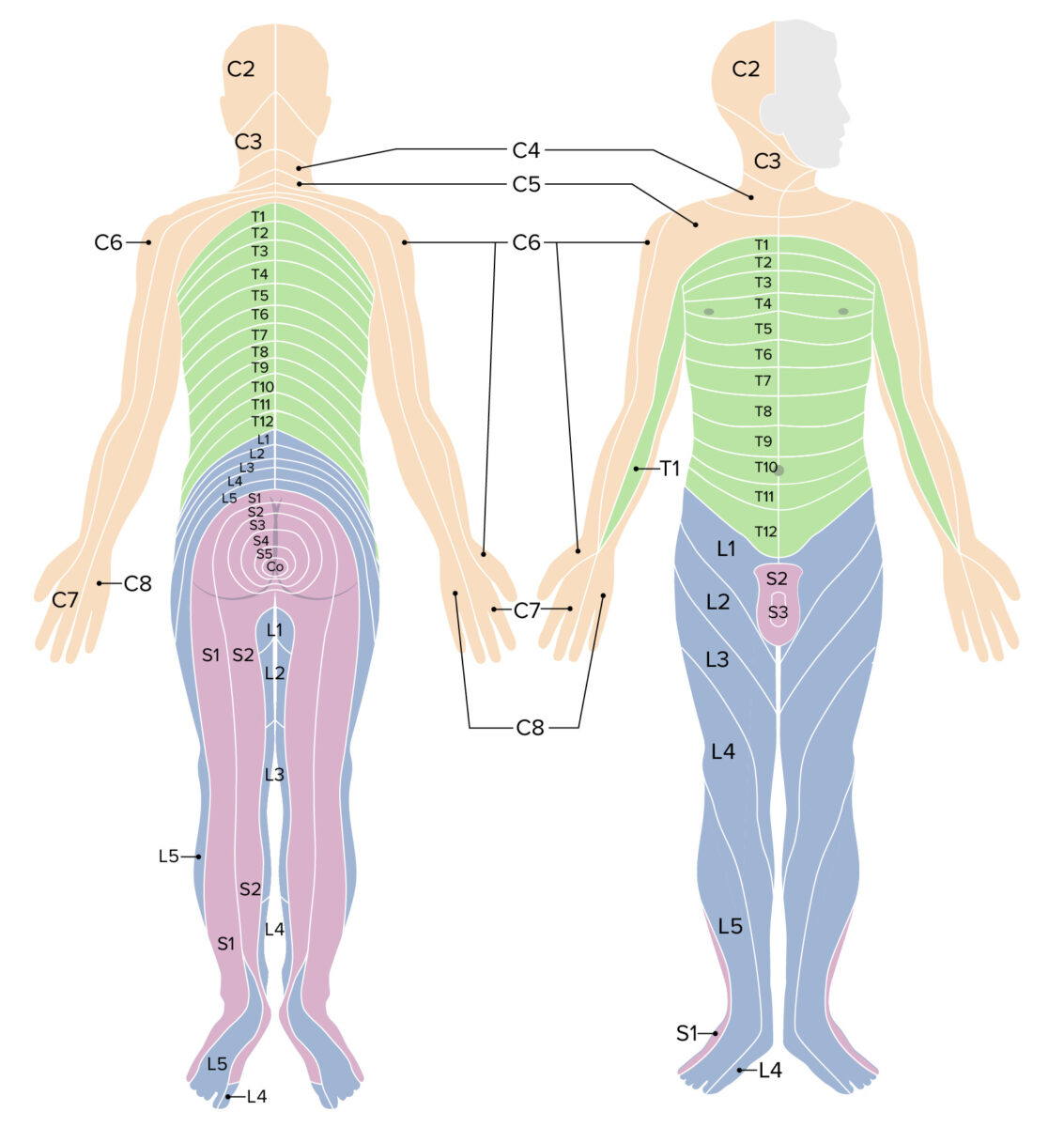



Spinal Cord Concise Medical Knowledge



Dermatomes Diagram Spinal Nerves And Locations




The Management Of Radiculopathy Neurogenic Claudication And Cauda Equina Syndrome Surgery Oxford International Edition



1



The Thoracic Level Chapter 3 Spine Disorders



Understanding Nerve Pain Through Spine Anatomy Absolute Injury And Pain Physicians




Spinal Nerves Anatomy And Functions Simply Psychology



Spinal Cord Injury Levels Cervical Thoracic Lumbar Sacral Sci




Myotomes And Dermatomes Week 3 Diagram Quizlet




What Are Examples Of Dermatomes




Neurological Examination Spinal Cord Part 3 Everything You Need To Know Dr Nabil Ebraheim Youtube



Peripheral Nervous System Ppt Video Online Download
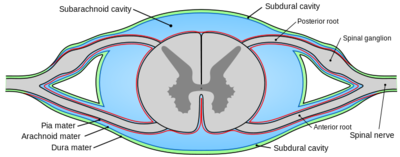



Thoracic Spinal Nerves Physiopedia



2




Spinal Nerves Anatomy And Functions Simply Psychology




Neurotrauma Review Series Part 3 What S In A Dermatome
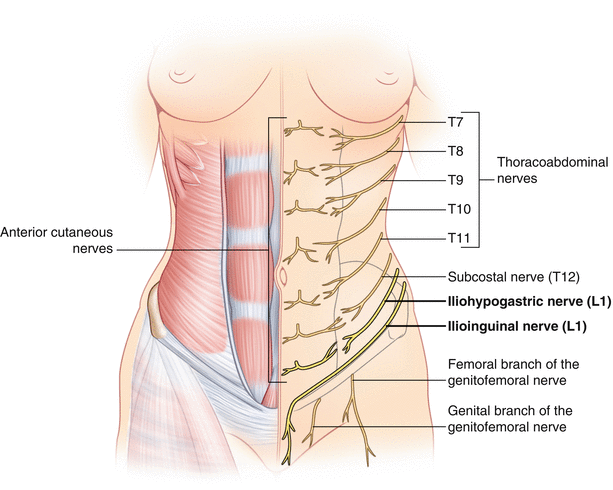



Intercostal Nerve Entrapment Chest Wall Springerlink




Spinal Cord Injury Levels Classification Travis Roy Foundation
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/l3-dermatome/TKW4cScsaH6iinBnwDISow_L3.png)



Dermatomes Anatomy And Dermatome Map Kenhub




The Spinal Nerves Shandong University Liu Zhiyu General Description 31 Pairs Spinal Nerves Cervical Nerves 8 Pairs C1 C8 Thoracic Nerves 12 Pairs Ppt Download




Vertebrae Etobicoke Interactive Spine Kipling Chiropractic Centre
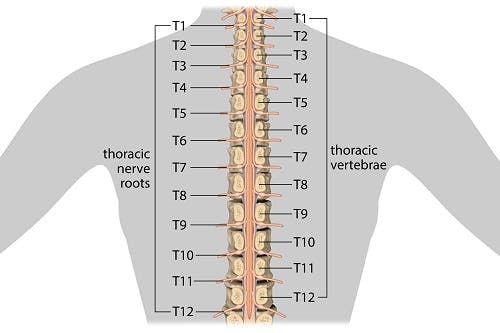



Spinal Cord Injury Levels Cervical Thoracic Lumbar Sacral Sci
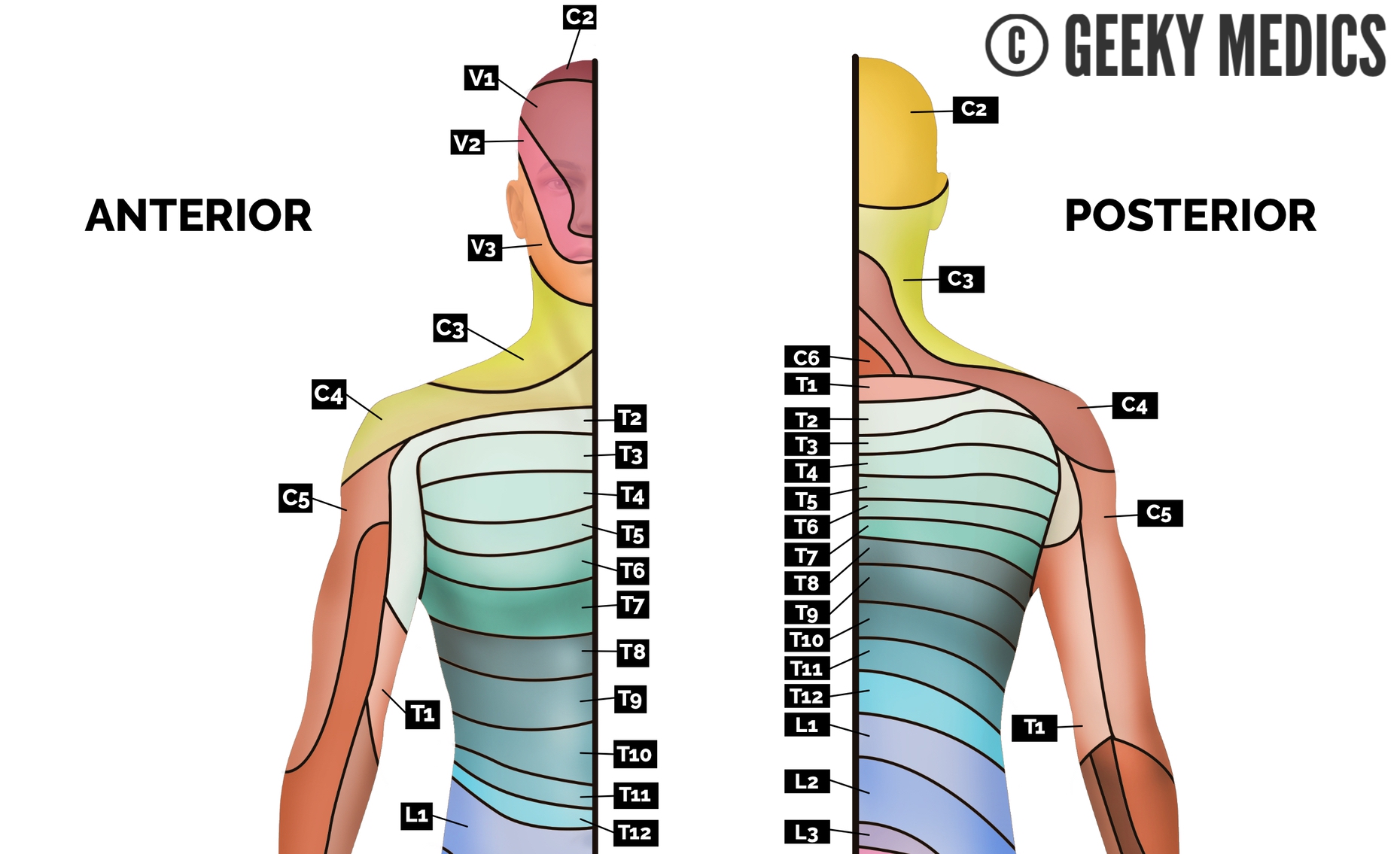



Dermatomes And Myotomes Sensation Anatomy Geeky Medics




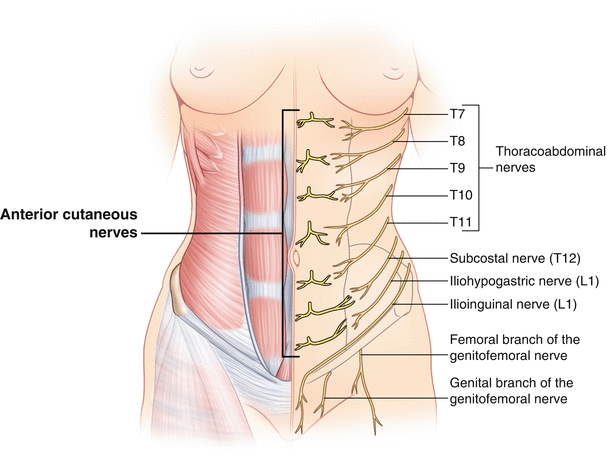
Anatomy Of Abdominal Anterior Cutaneous Intercostal Nerves With Respect To The Pathophysiology Of Anterior Cutaneous Nerve Entrapment Syndrome Acnes A Case Study Sciencedirect




Spinal Cord
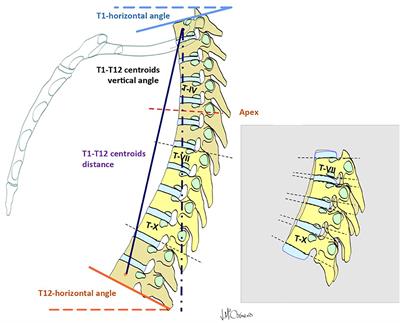



Frontiers Non Uniform Segmental Range Of Motion Of The Thoracic Spine During Maximal Inspiration And Exhalation In Healthy Subjects Medicine



What Happens When The Dorsal Root Is Damaged Quora
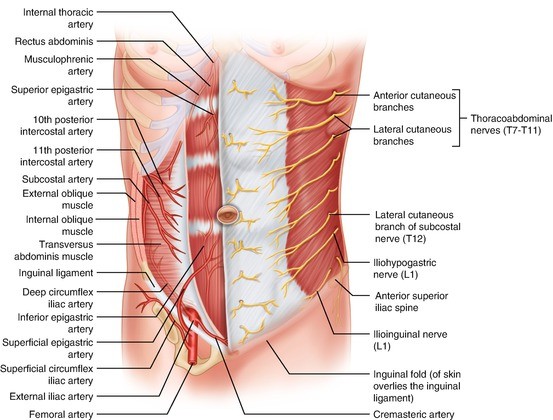



The Umbilicus Springerlink



Spinal Cord Injury Levels Cervical Thoracic Lumbar Sacral Sci




Pin On Rucken Wirbelsaule




Intercostal Nerve Block Landmarks And Nerve Stimulator Technique Nysora Nysora




Intercostal Nerves Wikipedia




Your T11 T12 Vertebrae Clearview Chiropractic




Lecture 8 Neurovasculature Of The Trunk Flashcards Quizlet




Inguinal Regional And Hernia Osce Station 10 Anatomy For The Frca



Interactive Parts Of The Spine Vertebrae Sections Spinal Cord Levels
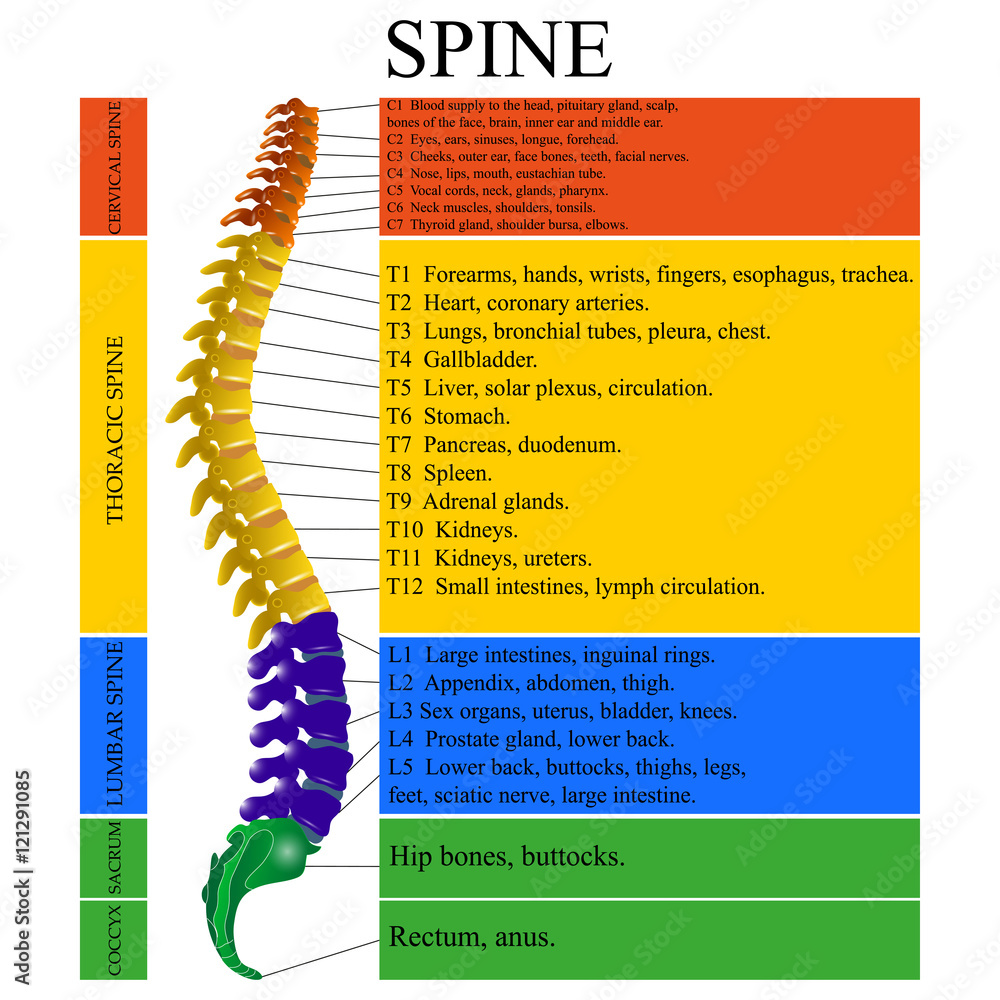



Diagram Of A Human Spine With The Name And Description Of All Sections Of The Vertebrae Vector Illustration Stock Vector Adobe Stock
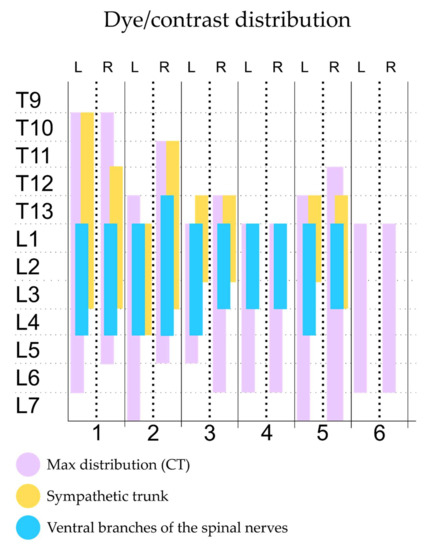



Animals Free Full Text Evaluation Of High Volume Injections Using A Modified Dorsal Quadratus Lumborum Block Approach In Canine Cadavers Html




The Mean Number Of Rootlets Composing Each Spinal Nerve Root In 32 Download Scientific Diagram
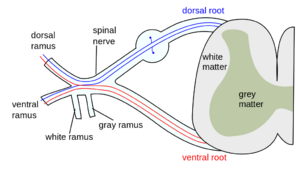



Thoracic Spinal Nerves Physiopedia




Spinal Nerve Levels Sagittal Mri Stock Image C030 3581 Science Photo Library
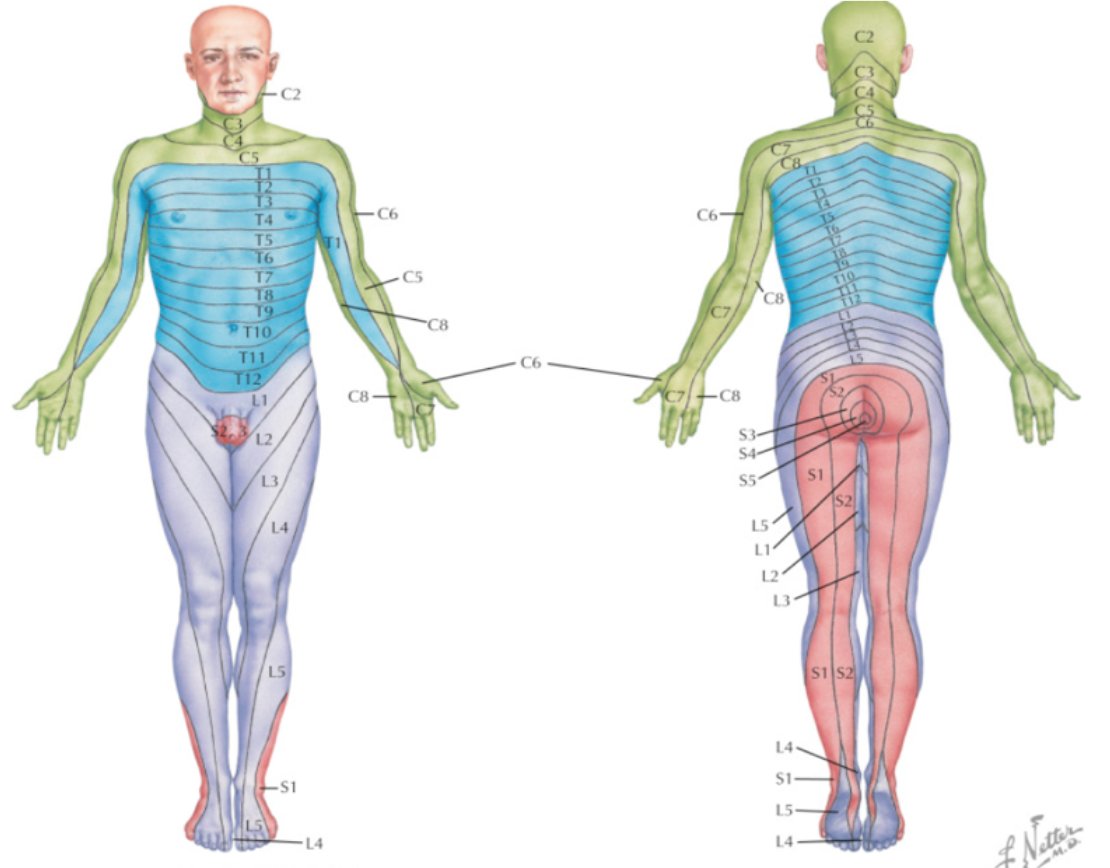



Brainbook 36 Let S Look Closer Into Some Anatomy The Adult Spinal Cord Terminates At The Level Of The L1 L2 Vertebrae The Lower Distal Part Of The Spinal Cord Is Known
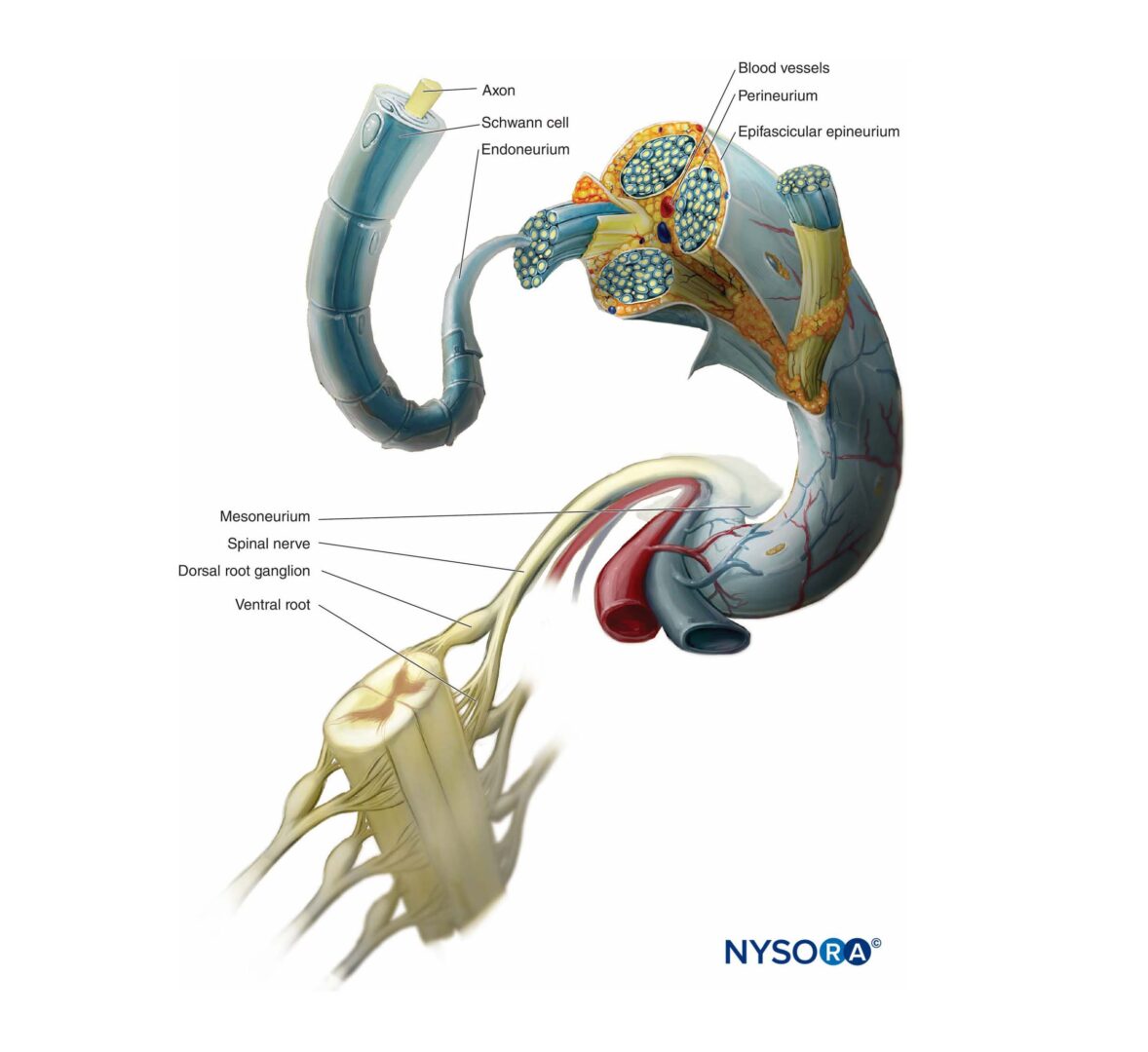



Functional Regional Anesthesia Anatomy Nysora Nysora
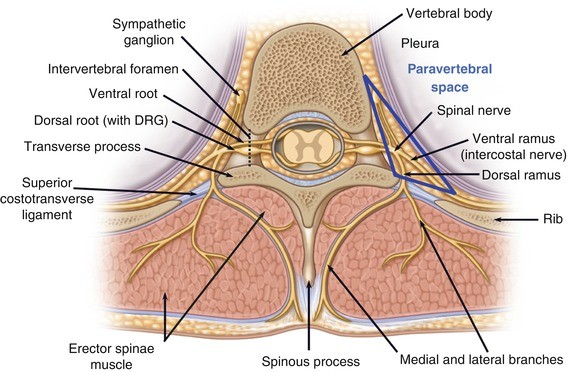



Clinical Anatomy Of The Trunk And Central Neuraxis Springerlink




Spinal Cord Injury Levels Classification Travis Roy Foundation
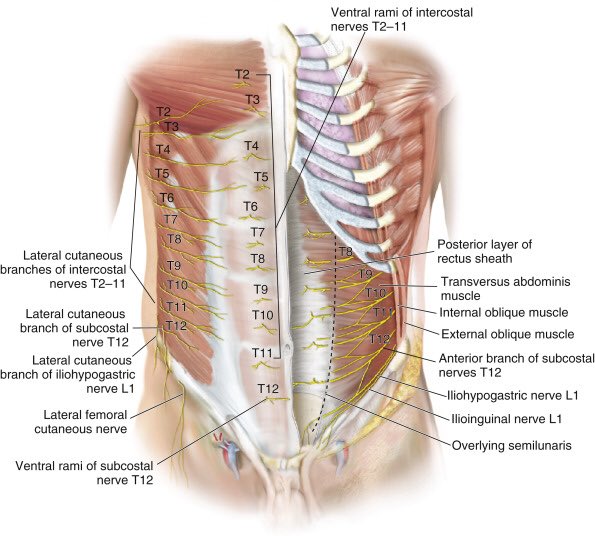



تويتر Cirbosque Some4surgery على تويتر Nerve Supply Of The Abdominal Wall Some4surgery Medtwitter Juliomayol Swexner Pferrada1 Herniacompleja Pipecabrerav Misirg1 Almagoch Cirugiauis Salo75 Drthawaba T Co C4q602pnxn
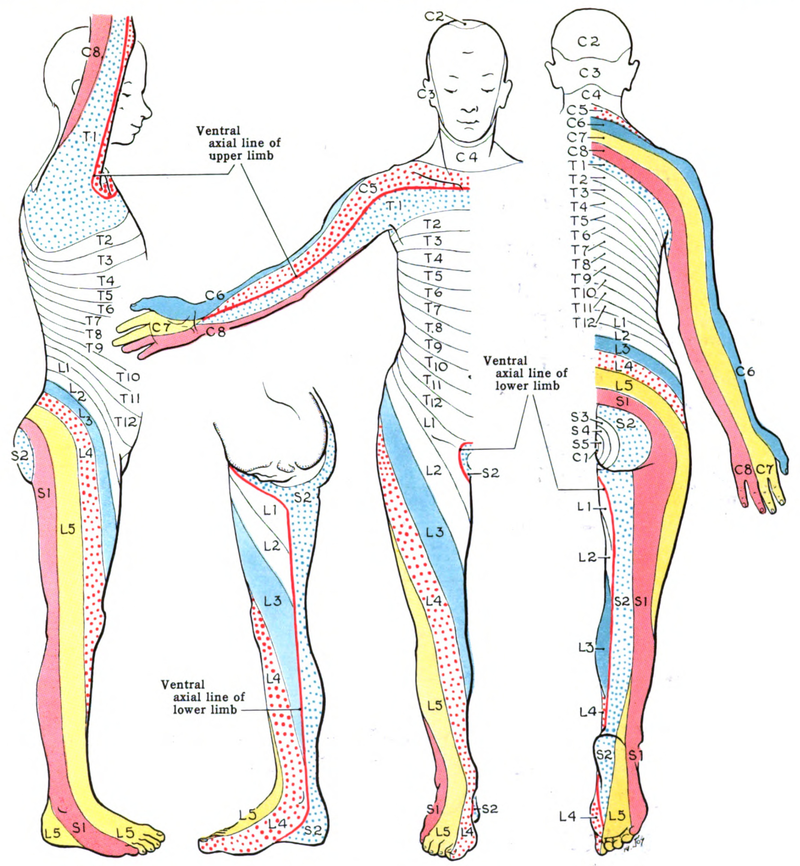



Dermatome Anatomy Wikipedia



T9 T12 Vertebrae Thoracic Spinal Cord Injury Spinalcord Com




T11 T12 Medial Branch Block In Patient With L1 Compression Fracture Download Scientific Diagram




Thoracic Spinal Nerve 12 Wikipedia
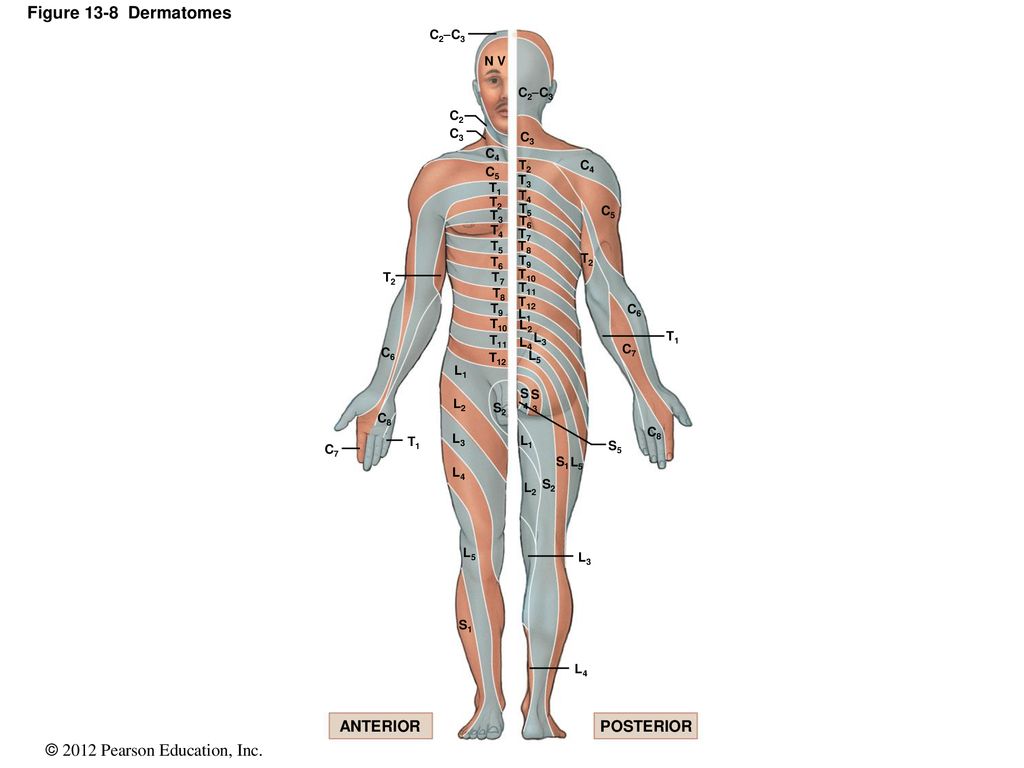



13 The Spinal Cord Spinal Nerves And Spinal Reflexes Ppt Download




Spinal Nerves Anatomy And Functions Simply Psychology




Unit 28 Abdominal Wall Flashcards Practice Test Quizlet




Spinal Cord Injury Levels Classification Travis Roy Foundation




Surgical Disciplines Most Of Surgeons Forget Abdominal Wall Nerve Supply Facebook
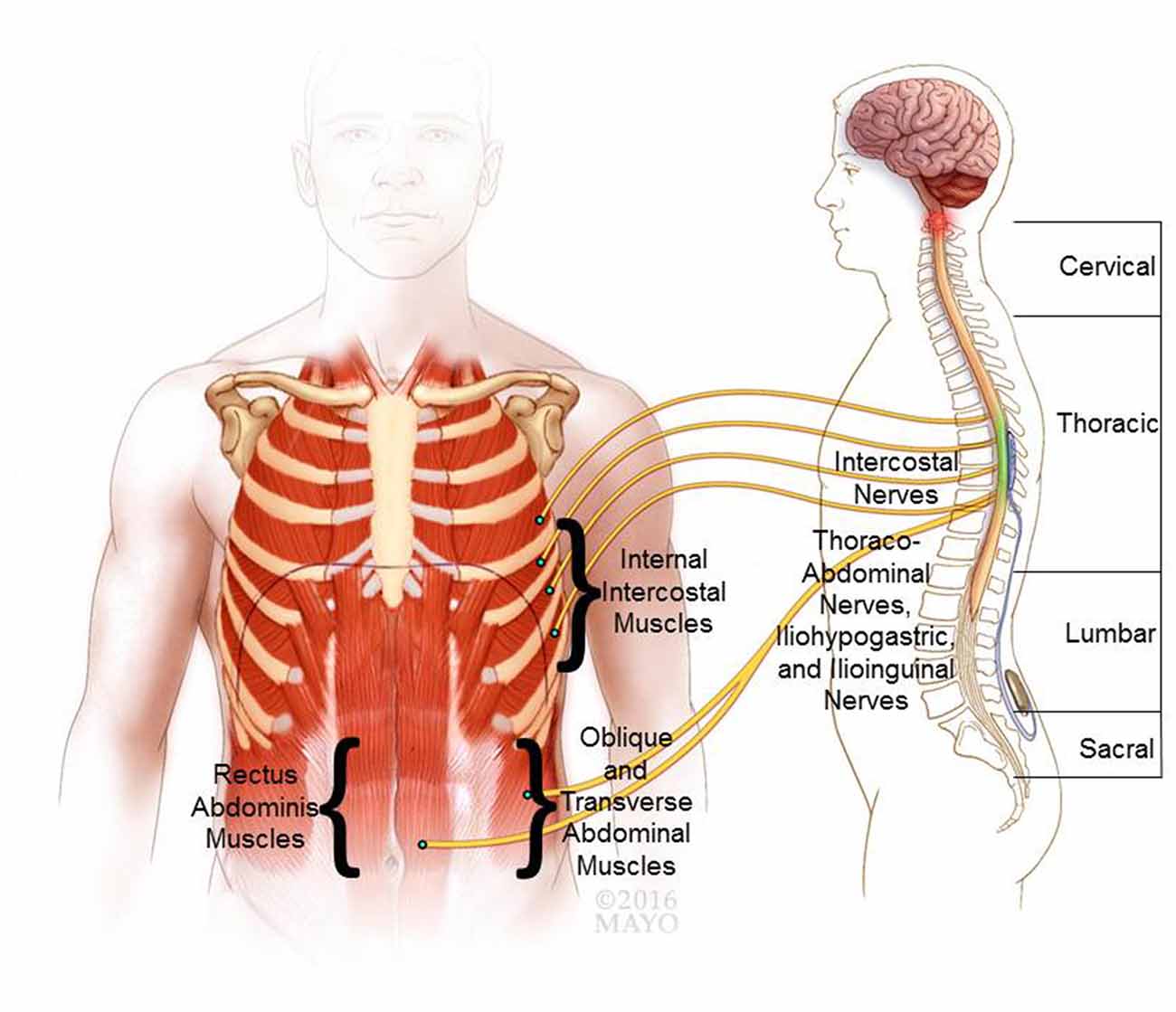



Frontiers Review Of Epidural Spinal Cord Stimulation For Augmenting Cough After Spinal Cord Injury Human Neuroscience
コメント
コメントを投稿